In October 2009, BASF introduced the new polymeric solubiliser Soluplus, a graft copolymer comprising polyethylene glycol, polyvinyl caprolactam and polyvinyl-acetate. Its unique chemistry coupled with its granular and solubilisation characteristics are very important in the development of solid solutions by hot-melt extrusion.
Hot-melt extrusion, a process used to disperse or dissolve a drug in a molten polymer, has become increasingly important in pharmaceuticals due to the possibility of dissolving poorly soluble drugs in a solid solution. Due to its flowability and extrudability, Soluplus is well suited to hot-melt extrusion.
Most of the current drug candidates in the development pipelines are barely soluble by regular solubilisation methods and therefore not sufficiently absorbed from the gastrointestinal tract. Thus, many promising drugs are not able to reach the market.
Soluplus significantly helps the pharmaceutical industry to develop and produce innovative medicines containing poorly soluble substances with low bioavailability that could, otherwise, not be formulated using conventional excipients. As a result, the excipient is now opening new doors in the field of pharmaceutical innovation.
solubilisation capability
To show its superior solubilisation properties, the solubilisation capacity of several solubilisers was determined in duplicate by means of saturation solubility in buffer media at pH 7. To do this, a 10% w/w polymer solution was over-saturated with an individual drug and stirred for 72 hours at room temperature. The resulting suspension was filtered through a 0.45µm filter and the amount of dissolved active in the filtrate was detected and measured using UV spectroscopy (Hewlett Packard 8452A). The saturation solubility was expressed as a mean value in g/100 mL.
The poorly soluble drugs used were: estradiol, piroxicam, clotrimazole, carbamazepine (all from Pfannenschmidt, Germany), griseofulvin, cinnarizine, itraconazole, danazole (all from Selectchemie, Germany), ketoconazole and fenofibrate (both from Sigma Aldrich, Germany).
The solubilisers used were: Soluplus, Solutol HS15, Cremophor EL, and Cremophor RH40 (from BASF SE, Germany). Vitamin E-TPGS and Tween 80 were obtained from Eastman and Croda, US, respectively.
Next, extrusion studies were performed on an extruder (PTW 16, ThermoFisher Polylab) equipped with 16mm co-rotating twin-screws at a feed rate of 1kg/h and a barrel temperature of 150°C.
Dissolution studies on fresh and stored extrudates, each containing 100mg of active, were carried out and compared with the pure crystalline active. The determination was performed in triplicate using USP apparatus 2 at 50rpm in 700mL hydrochloric acid (0.1 molar). The resulting data shown are mean values ± standard deviation.
The bioavailability study was performed on beagle dogs in the fasting state using itraconazole dosed at 10mg/kg body weight. Three formulations filled in hard gelatin capsules containing the drug and a disintegrant (Ac-Di-Sol, FMC Biopolymers) were tested. The formulations were:
- i. crystalline drug substance (95% active, 5% disintegrant);
ii. a physical mixture of active and Soluplus (15% active, 80% Soluplus, 5% disintegrant)
iii. a solid solution of active and Soluplus manufactured by hot-melt extrusion (95% solid solution, 5% disintegrant, 15% active, 85% Soluplus).
solubility results
For all actives examined, an increase in saturation solubility was observed with Soluplus. The saturation solubility in 10% solubiliser solution ranged from 0.013g/100mL for itraconazole to 0.35g/100mL for carbamazepine. In comparison, the saturation solubilities for the pure actives in water were all below 0.08g/100mL. In certain cases, e.g. for estradiol, danazole or fenofibrate, the saturation solubility increased >100-fold in polymer solution.
The solubilisation benchmark in phosphate buffer pH 7 showed a significant solubilisation effect with Soluplus for all actives examined (see Figure 1). In the four model drugs studied, Soluplus outperformed the other solubilisers and achieved the best results. The extrusion experiments conducted in this study led to transparent and clear extrudates for itraconazole and fenofibrate.
X-ray powder diffraction (XRPD) analysis revealed no crystallinity in the freshly extruded solid solution. Furthermore, the extrudate stored for three months under different storage conditions was clear and transparent, suggesting that the drug was completely miscible in the solid solution and remained stable under the accelerated conditions (40°C/75% RH; glass bottle with PE lid), with no apparent crystallisation.
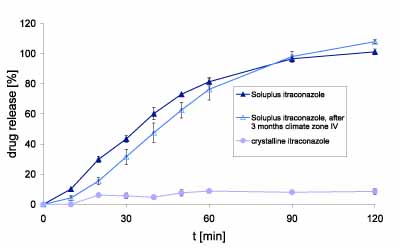
Figure 2: Drug release of itraconazole compared with crystalline substance and after storage at 40°C/75% RH for three months
Dissolution testing of crystalline itraconazole in 700mL HCl showed about 4% release within two hours, which approximates the saturation solubility of the active (Figure 2). In comparison, the fresh extrudate showed complete release and achieved over-saturation within two hours. Likewise, the extrudate stored for three months under accelerated conditions (40°C/75% RH; glass bottle with PE lid), showed an identical release profile to the fresh extrudate.
bioavailability results
The results of the bioavailability study can be seen in Figure 3, which illustrates the plasma concentration over time following separate oral administration of each formulation.
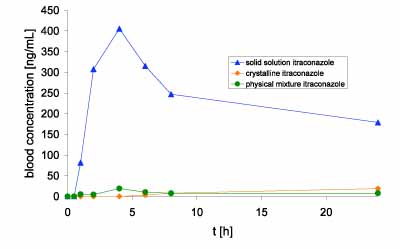
Figure 3: Blood concentration of itraconazole in beagle dogs
The solid solution of itraconazole in Soluplus led to >20-30-fold increase in the area under the curve (AUC) as compared with crystalline or physical mixture formulations. Soluplus in the pure physical mixture did not influence the AUC of itraconazole; and the curve progression was comparable to the progression after the administration of the crystalline active.
Soluplus has been specifically designed to solubilise poorly soluble APIs and has demonstrated an excellent capability to form solid solutions with many crystalline APIs. It combines the advantages of solid solutions and solubilisation in one, which can help to increase the bioavailability of insoluble actives.
Due to its excellent capability to dissolve poorly soluble drugs and form solid solutions, Soluplus is suitable for innovative processing technologies such as hot-melt extrusion.
The safety of the new polymer can be demonstrated with comprehensive documentation. All these features result in more cost-efficient processing of drugs for the manufacturers and more stable and convenient dosage forms for patients. Even though Soluplus was developed for solid solutions, it can be used for other applications too. Besides hot-melt extrusion, drug layering and spray drying, it can be also applied as a binder in wet granulation or dry binder in direct compression.
With multiple applications like these, you stand to benefit from the solubilisation capabilities of Soluplus while using it in standard processes.
Sources
BASF’s Soluplus achieves silver at the CPhI Innovation Awards
in Paris
BASF won the silver award for its excipient Soluplus, a new chemical entity and said to be the first excipient in the market specially designed to form stable solid solutions via hot-melt extrusion. It has solubilisation properties and offers enhancement in the drug release and bioavailability of poorly soluble APIs.
Vanessa Occhipinti (pictured below) accepted the silver CPhI Innovation Award on behalf of BASF at the exhibitor party in Paris.

Vanessa Occhipinti
