Shimadzu have applied the dual-polarity MALDI-TOF detection on synthetic oligonucleotides corresponding to the CFTR gene sequence known to be the mutation which causes cystic fibrosis.
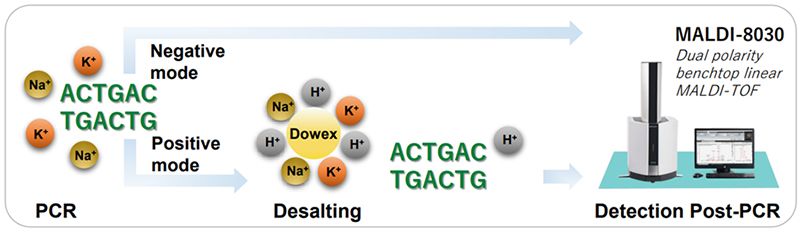
The compact and versatile MALDI-8030 utilised the dual polarity feature which enabled the negative ion mode to circumvent issues often associated in positive ion mode. As oligonucleotides can form sodium or potassium adducts in solution by positive ion mode, the sensitivity can be drastically reduced. Additionally, positive ion mode needs a lengthy desalting protocol to diminish the adduct formation. Negative ion mode resolves these common problems with ease.
Negative ion mode offers numerous advantages. It offers a simpler, faster workflow than gel electrophoresis, and eliminates the desalting sample clean-up step necessary in positive ion mode. There is a reduction of salt adducts which significantly eases data interpretation by removing these interferences, and finally, it offers good, reproducible signal sensitivity.
This methodology easily identified the wild type, homozygote and heterozygote of the mutated gene sequence known to cause cystic fibrosis. The results exceed current practices used for oligonucleotide analysis. This approach could easily be taught to students in teaching laboratories and for more routine laboratories for genotyping. For more information on the MALDI-8030, please visit shimadzu.co.uk/maldi-8030.