UMass Lowell has opened a state-of-the-art lyophilisation facility that will help drive innovation and discovery in biopharmaceutical manufacturing in New England and beyond.
Called the Lyophilization Research Bay, or LyoBay, the new lab is the first pilot-scale facility on the East Coast that is located in a cleanroom environment and is accessible to outside users. The LyoBay is expected to pave the way for more efficient industrial processes, better manufacturing practices and higher-quality life-saving products such as vaccines, biologics and other injectable therapeutic drugs.
Lyophilisation, also known as cryodessication or freeze-drying, is a process that removes water from sensitive, perishable materials (in this case, biopharmaceuticals) to make them more stable and extend their shelf life, as well as making the materials easier to store, transport and use.
The process works by freezing the material, then reducing the air pressure and adding low heat to allow the frozen water in the material to sublimate (change directly from ice to vapor without melting). This is in contrast to conventional dehydration, which uses high heat to evaporate the water.
“Many biopharmaceutical companies don’t have their own pilot-scale freeze-drying facility,” says Chemical Engineering Prof Seongkyu Yoon, who will lead the research efforts for the university. “The LyoBay will create a lot of collaboration with pharma companies as they go from product R&D to commercial manufacturing. They will come to UMass Lowell to use our facility, which will create research partnership opportunities for our faculty and students.”
Training the Future Workforce
The LyoBay, which is in a cleanroom at the Saab Emerging Technologies and Innovation Center on North Campus, was developed with $1.3 million in funding from the Massachusetts Life Sciences Center and $120,000 from the National Institute for Innovation in Manufacturing Biopharmaceuticals (NIIMBL), a Manufacturing USA network institute that works to advance US leadership in advanced manufacturing.
NIIMBL also provided about $640,000 in funding for the creation of tools to support the lyophilisation process scale-up. Additional in-kind support from partnering research institutions and industry collaborators contributed to this project.
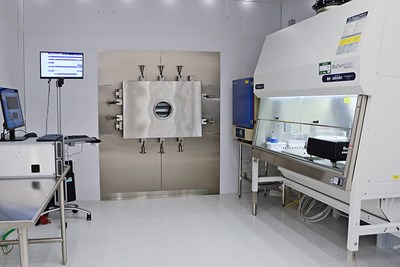
UML's new Lyophilization Research Bay, or LyoBay
A NIIMBL-funded project team – led by Physical Sciences Inc. (PSI) of Andover and including UMass Lowell, the University of Connecticut, Purdue University, Merck and Genentech – was instrumental in establishing the LyoBay and will be the first user of the facility.
“This is an example of a great partnership between academia, industry and government,” says Julie Chen, vice chancellor for research and economic development. “This is so important in expanding biomanufacturing here in Massachusetts.”
The centrepiece of the LyoBay is the 7,000-pound SP Scientific LyoConstellation S20, a high-capacity freeze-dryer with a total shelf area of nearly 21 sqft inside its airtight, stainless steel chamber.
The unit’s refrigeration and vacuum system can bring the chamber’s shelf temperature down to –60oC(–76oF) and its system pressure to as low as 15 millitorr, about two hundred-thousandths of the atm at sea level.
The LyoBay will serve as a research testbed for preclinical process monitoring, development and scale-up, as well as for testing new process analytical technologies. It will also provide training to support the regional and national biotech industries, according to Yoon.
“We will prepare the future workforce in the field by developing hands-on, freeze-drying training programmes using the LyoBay,” he adds.
A Rare Resource
The LyoBay is the latest addition to UMass Lowell’s Core Research Facilities, which also include the Nanofabrication Lab, the New England Robotics Validation and Experimentation (NERVE) Center, the Fabric Discovery Center, the Materials Characterization Lab, the Next-Generation Sequencing & Genomics Lab, the Analytical Chemistry Lab, the Nuclear Magnetic Resonance Spectroscopy Facility, the Radiation Laboratory and the Thermal Analysis & Materials Property Lab.

The LyoBay's high-capacity freeze-dryer. (L–R): William Kessler, VP of applied optics at Physical Sciences; Thomas Ferraguto, Director of UMass Lowell’s Nanofabrication Lab, and (PSI)
John Erickson, senior fellow at NIIMBL, said that while the goal of lyophilisation is to make medicine stable, the lack of sensors and computer models has hindered the researchers’ understanding of industrial lyophilisation, resulting in inefficient, suboptimal processes.
“NIIMBL has funded projects to improve our understanding of new sensors and models, but they need to be tested in a full-size lyophiliser. But the problem is that industrial lyophilisers are busy making medicine – you can’t just go in and do whatever you like,” said Erickson. “This is where the LyoBay comes in. It is a very rare resource that will allow us to test these innovations and future innovations in a realistic setting.”
“The LyoBay will lead to new development sensors, freeze-drying models and processes and workforce training to enable us to continue providing the newest biopharmaceutical treatments to patients worldwide,” said Green. “It will allow R&D experimentation to progress at a faster rate and support collaborative studies with both academia and users. This will lead to improved results and better understanding of the scale processes, resulting in higher product quality for all of us.”
